How is a formula 1 car manufactured?We explain it to you
Load audio player
How many pieces does an F1 car have?
A formula 1 car is made up of 14,500 individual components.
The equipment manufactures a new one every year and, although each design is unique, it conforms to a series of standards that define dimensions, prohibited areas, weight limits and specifications of the materials.
To maintain reduced costs, cars must carry certain standard and prescribed parts, while transferable pieces - which include exchange boxes and clutches - can be bought and sold between equipment.
From 2022, cars must carry certain "standard" pieces and "prescribed" pieces, such as wheel aerodynamics, wheel cubes and front floor tray, which equipment must build according to an established design.There are also "transferable pieces", such as exchange boxes and clutches, which can be bought and sold between equipment.
The technical regulation defines "rules of rules" that limit equipment designs.This includes the establishment of specific dimensions for ailerons and bargeboards, the definition of prohibited aerodynamic areas and the prohibition of certain high -cost alloys in the engines.
Every year there is a new car, but unlike a road car, which is usually the same once it leaves the factory, an F1 car develops continuously, with new pieces that enter race to race.
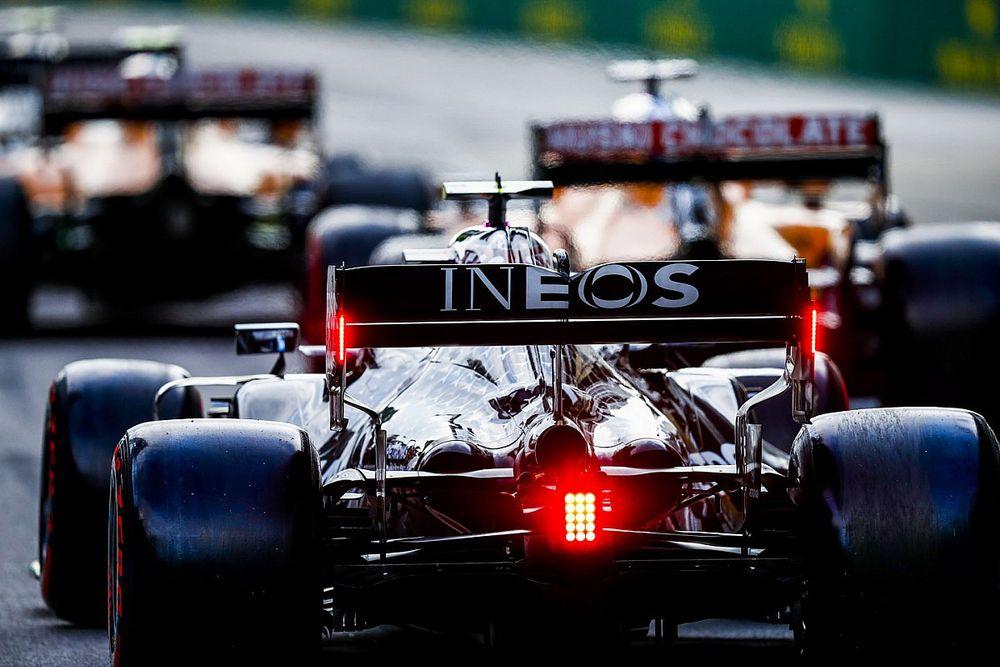
An F1 car on the track.
Photo by: Mark Sutton / Motorsport images
When does the process begin?
The design of an F1 car takes much longer than you think.The best teams begin to work in the new cars more than one season before they go on track, for example, the work in a 2021 car would have started in the last months of 2019.
The process begins with motor and chassis team leaders discussing the general approach and receiving the comments of the pilots on the current car.After that a concept team evaluates the new approaches.
As the year prior to the launch of the car progresses, the design becomes more complicated and more detailed, and the equipment approach slowly moves away from the development of the current car to produce the future car.
Throughout the season, more and more staff moves from the design to work in the new car, but only in winter things join physically, with the test of externally manufactured elements and designs turned into real pieces.
Design and development
The development of a car begins in the design office, where the teams of people sit behind CAD computers (computer assisted design) to produce complex 3D drawings of the new pieces, which, at a peak, can reachbe hundred every day.
Different subgroups are responsible for different areas or aspects of the car, such as transmission, electronics, mechanical design and aerodynamics, as well as the design of compounds, which implies the planning of the way of manufacturing the pieces.
Aerodynamics is one of the most important areas and teams usually have between 3 and 4 separate groups, each focused on a different area of interest.They create designs that are tested on CFD (Computer Fluid Dynamics) to decide which ones pass to the wind tunnel tests.
In the past, some equipment tested real -scale cars in wind tunnels, but now the maximum is set at 60% to reduce costs (since the pieces cost much more real than 60%).

Most model parts are now manufactured with rapid prototypes and 3D printing, and wings are metal.In the tunnel, the car is screwed to a central column and a fan blows air with a belt underneath.
The model is full of sensors to record speed and pressure, and the spine is linked to a sensitive balance to measure the descending force.The car moves dynamically to change the height and inclination of the body, with movements that would be similar to those of being on a track.
Now the equipment is limited to a single tunnel -in the past, it is known that Ferrari ran 24 hours a day in three places!- And the speed is limited to a maximum of 180 km/h, which means that they cannot completely try all aspects of the car performance.
There are also limits in the amount of time that can be dedicated to the CFD and the wind tunnel, depending on the place where a team ended the previous season.The last classified gets 25% more time in the tunnel than the current champion.
An F1 model on a scale ready for the wind tunnel.
Photo by: Manor Racing
Manufacturing
About 80% of the car is made of compound materials and pre -impregnated carbon fiber is the main material.This tissue carbon wire mats previously covered with resin is supplied in giant rolls and is stored in freezers to keep it fresh.
Carbon fiber parts begin with a pattern, usually made of epoxy with five -axle milling ones that use CAD data to cut with a 0.05 mm accuracy.Next, the patterns are used to manufacture a female carbon fiber mold, which is then used to make the final piece.
The areas of manufacturing compounds of a F1 factory are clinical environments with air pressure controls, humidity and temperature and workers always carry clean protective monkeys and footwear protectors.This is because any impurity that enters the piece could cause a catastrophic failure.
As an example of figures, McLaren has 130 people working on the composite pieces at all times, in the white room, in the cutting and assembly workshops, in the employer workshop and in the mechanical workshops.Smaller teams subcontract this manufacturing process.
The carbon fiber mat is accurately cut into specific ways - defined by the compound design department - and are placed very precisely, since the different directions of the filaments offer different properties and resistance addresses.
The placement of the pieces continues to be made by hand, with the help of a computer laser placement system.More layers are used in the pieces that support more tension, and some pieces, such as chassis, have different thicknesses in different areas according to stiffness requirements.
In fact, the complex nature of the manufacture of carbon fiber has allowed the equipment to skip the rules - literally - creating winging that are weaker in certain areas and that can be flexed by exercising a certain aerodynamic load passing the static load tests, but flexing on the track.It is said that Mercedes's rear spoiler did this at the end of 2021.
Once the carbon is placed in the mold, it is introduced into a vacuum bag, it is placed in an autoclave (a large oven) and under pressure.Then heals at a controlled temperature and pressure for hours.
The high temperatures of the autoclave melt the resin between the carbon threads so that it extends and then hardens until a solid piece.The number of vacuum treatments and thermal curing processes can also affect the final piece.
Many pieces are manufactured in two or more sections: the monocoque chassis, for example, consists of two halves (upper and lower) that stick together;The front and rear fins are hollow and stick together to obtain the final construction.
Together with the carbon fiber process, there is also a lot of metal manufacturing, largely using "exotic" metals.Alpine, for example, uses 16 machines to process all these pieces and replaces them every three years.
Andrew Scrowther, CNC Machinist, McLaren
Photo by: McLaren
Piece test
Remember the 14.500 pieces mentioned at the beginning?Well, all of them must be inspected and approved before they reach the car, and there is not only one piece of each one.
Before the car turns a wheel, numerous tests are carried out to guarantee the maximum possible reliability, and the number of participants in modern races, compared to that of 10 years ago, it shows that this works.
The materials are put under the microscope (literally) and all the pieces of the car are subjected to non -destructive tests (NDT) with X -ray techniques or ultrasound to evaluate the union of the joints and the state of the laminates, firmness checks,visual controls and thorough cleaning.
Also used computer coordinates (MMC) and manual laser devices are also.
A nose, for example, undergo an inspection of composite materials, a hexagonal laser scan, to a non -destructive test of composite materials to check the cracks by meansphysical tension.
Next, all sub -consumption and sets are assembled and started in dynamic test banks that submit to the pieces to tests that coincide with the temperatures and movement cycles that are expected on the track.
Each piece is assigned a "life" based on mileage or time, after which it must be removed and replaced, and the components, especially security critics, are often tested up to three or four times in theLife time that must last, just to be sure.
Teams must also include an increasing number of shock structures around the car.FIA shock tests must be overcome before the car is certified.These include front, rear and lateral impact tests, and are extremely destructive.
First launch
This is when everything becomes a reality.In the factory, the power unit, the fuel system, the hydraulic system, the transmission and the cooling system are set to the chassis and connect to be tested.
At that time, the design process is halfway, so there is still much to go.The car does not yet have all the mounted body, so it is visually described as "robocop when the entire skin is removed".
Once all the pieces are made and ready to be mounted, the first car construction lasts approximately one week, with the car mounted on the racing bay.The monocoque chassis is the central section, and all sub -couples are screwed.
A view of the Barcelona circuit line.
Photo by: Mark Sutton / Motorsport images
Shakedown and Testing
It is the first time that the car leaves the garage in a circuit.The teams must make a "Shakedown" of the car to make sure that it is well screwed and can circulate without problems.
The teams usually do this in a "designated day", with a limited route to less than 100 km.In this way it is ensured that the car works well and the equipment can focus its limited pre -season test time on the tuning of the car before the first race.
How much does it cost to make a F1?
At present, Formula 1 has a cost limit, so the expense is limited to 140 million dollars, or 106 million pounds, per season in 2022, and subsequently reduced to 135 million dollars, or 102 millionof pounds, from 2023.
This budget must cover all the costs related to the performance of the car, but not the marketing or the salaries of the pilots and the three most expensive members of the team.
The cost of the car itself is difficult to define due to all the different elements that intervene, and that each team varies its design, of course, but it is estimated at about 8 million dollars.
The engines are the most expensive part, with an estimated cost 4.73 million dollars per unit.
The chassis costs around 1.35 million dollars.
The gearbox costs 1 million 13 thousand dollars.
Front wings can be worth 202 thousand dollars each, and many are needed in the season!
The steering wheel, thanks to its complex electronics, costs about 67 thousand dollars.
And although the tires look like a bargain comparative.
After all, F1 cars are probably the most detailed in history, and they certainly cost a lot of money, but it is this attention to detail that gives us some of the best races in the category seen in recent years.
También lee:compartidos comentarios


























Types of Hats for Kids: The Perfect Hat for Every Occasion
19/05/2022When it comes to dressing up your kids, hats are a great way to add some personality and style. There are so many different types of hats for kids available on the market today, that it can be hard to...